When having your own website, it’s vital to focus on security, especially if you have a large base of customers and users who visit the site and register with personal data daily. But how do we make our domain secure? Simple, with a DNSSEC, which we will talk about in this post.
To learn more, you should know that domain security is fundamental to maintaining the general security and reliability of the Internet, protecting users and their information, and increasing confidence in online transactions and communications.
Now that you know this, you must know what DNSSEC is and how it can help increase the security of your domain. Keep reading this post until the end, and don’t miss anything.
What is DNSSEC?
The standard DNS (Domain Name System) has a set of extensions called DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) that increase security. The main objective of DNSSEC is to defend against specific cyber-attacks, such as cache poisoning, digitally signing DNS data, and allowing web browsers to confirm the validity of the information they receive from the DNS server.
Without requiring significant system changes, DNSSEC can be implemented on top of the existing DNS infrastructure because it’s scalable and adaptable by design. With several Top-Level Domains (TLD) already signed and more in the process of being signed, DNSSEC is being used more and more frequently.
DNSSEC signs DNS records using public key cryptography, allowing a client to confirm that the information obtained from the DNS server is accurate and has not been tampered with. The customer can achieve this by comparing the digital signature with a “chain of trust“.
In short, DNSSEC strengthens the overall security and trust of the Internet by adding an additional layer of security that helps defend against specific types of cyber-attacks.
How does It Work?
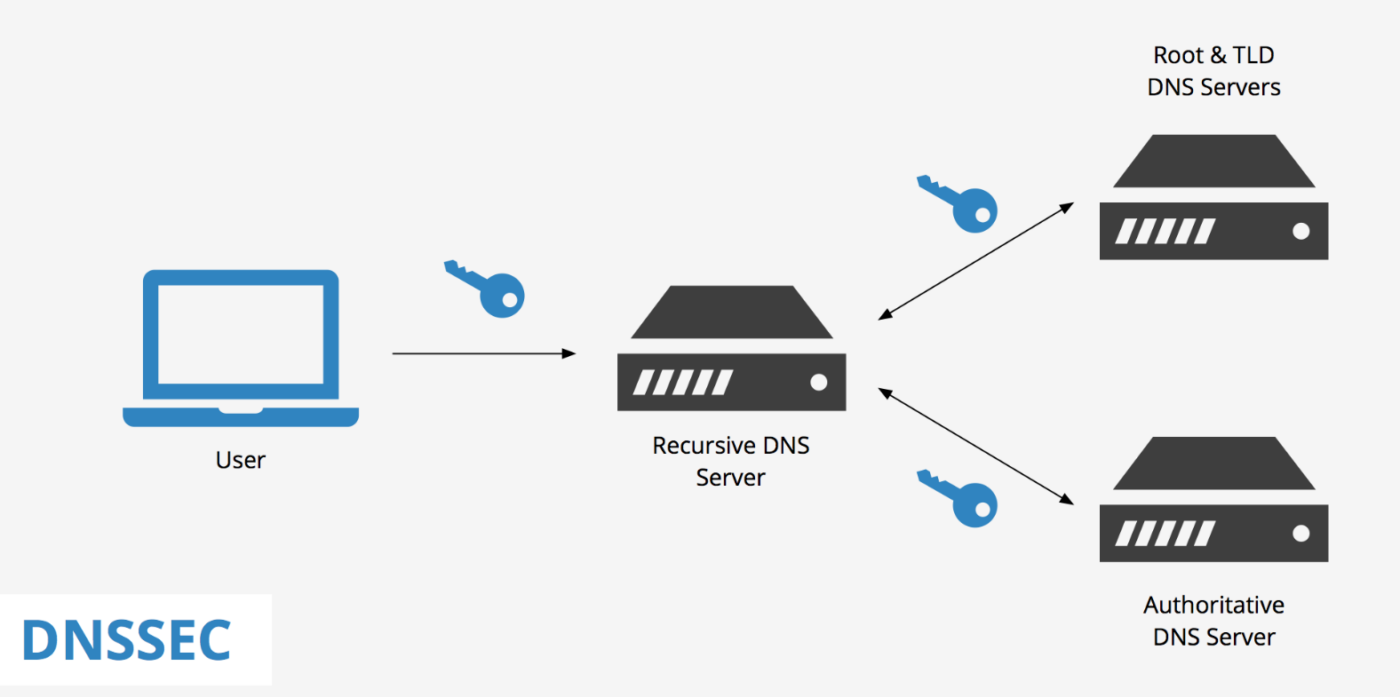
Digital signatures and public key cryptography are used by DNSSEC to protect the DNS. The fundamental idea of this currently widely used set of extensions is to give the DNS an additional layer of security by allowing clients to confirm the validity of the DNS data they receive, as we mentioned previously.
This is how DNSSEC specifically works in a simple list that will give you a better idea of exactly how this set of security extensions works:
- The DNS zone administrator creates a public/private key pair and signs each resource record (RR) in the zone using the private key. DNS servers keep a copy of the signed RRs and the public key.
- When a client consults a DNS for a specific domain name, the DNS server returns the RRs for that name and a digital signature for each RR.
- The client then validates the signed RRs using the public key of the zone’s DNSKEY resource record. The customer can be sure that the RRs haven’t been tampered with or forged if the digital signature is valid.
- To validate the authenticity of the public key, the client must follow a “chain of trust” that starts with a trusted source, such as the public key of the root zone. The client can then validate the authenticity of the public key for the top-level domain (TLD), then for the second-level domain, and so on until it reaches the desired domain.
When and Why was DNSSEC Created?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), an Internet standards-setting body, initially described DNSSEC in 1997. Several RFCs (Request for Comments) were issued in response to the initial specifications.
DNSSEC was created to remedy security flaws in the original DNS architecture, which was not created with security in mind. DNSSEC has grown and changed over time to better adapt to the increasing security demands of the Internet.
The adoption of DNSSEC has been a slow process, with numerous companies and countries around the world finally adopting it and continuing to use it today. DNSSEC is now widely used and supported by many large enterprises and organizations.
DNSSEC functions
DNSSEC has some key functions that are really important, not only to ensure the complete security of the DNS protocols but also for the operation of DNSSEC itself. These two key functions are:
- Integrity protection: this makes it possible to recognize whether the data were originally signed owner and whether they have been modified in transit.
- Source authentication: Through source authentication, it’s verified that the data received come from the same area where they’re considered to have originated.
How do I know if my domain is DNSSEC compatible?

Not all domains are DNSSEC compatible, so it’s of vital importance to know if ours is or not, and for this, we have a large number of verification methods.
One of the ways to verify if your domain is DNSSEC compliant is by accessing Verisign’s DNSSEC – Analyzer website. When you log in, you’ll only have to include the domain you’re interested in knowing, in this case, for example, yourweb.com. We place it in the search engine, and after a few seconds, all the information related to it’ll be displayed, including its compatibility or not with DNSSEC.
You can also opt for another platform that works in the same way, such as DNSViz, in which we must also enter the name of our domain, search and wait a few moments for all the information to be displayed.
In addition, you can check your domain’s DNSSEC compatibility through other methods that do not require a website:
- Consult your domain registrar: Your domain registrar should be able to inform you if your domain is DNSSEC-enabled or if DNSSEC support is available. Note that some registrars may charge a fee for DNSSEC support.
- Check your DNS records: To see if your domain is DNSSEC-enabled, run a DNSSEC diagnostic test to examine your domain’s DNSSEC status and DNS records.
- Examine your TLD: You can check the list of top-level domains (TLDs) that have implemented DNSSEC on the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) website to see if your TLD is DNSSEC-enabled.
How do I enable DNSSEC?
The procedures required to enable DNSSEC and sign your zone may differ depending on your DNS software, so try to consult your domain’s instructions previously for additional details. In general terms, these are the steps you must follow to enable DNSSEC in your domain:
1. DNS preparation:
- Familiarize yourself with the fundamental ideas of DNSSEC, such as the different types of DNSSEC records and the signing procedure.
- Check if your DNS software supports DNSSEC.
- Create a key pair consisting of private and public keys to sign the zone.
2. Enable DNSSEC in your DNS software:
- Configure your DNS software to use DNSSEC.
- In your DNS program, import the key pair.
3. Sign your zone:
- Sign your zone using the key pair you’ve generated in your DNS software.
- Verify if the signing procedure was successful.
4. Make DNSSEC records public:
- Publish DNSSEC records, including DS (Delegation Signer), DNSKEY (DNSSEC Key), and RRSIG (DNSSEC Signature) entries, in your DNS zone.
- Check that the DNSSEC records have been published correctly.
5. Verify your DNSSEC configuration:
- To ensure that your DNSSEC configuration works correctly, use a DNSSEC validation resolution system.
- Check the validation results to make sure there are no problems or warnings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using DNSSEC
As perfect as this system may seem, DNSSEC has some disadvantages that aren’t really serious but can be important before activating it in your domain.
Advantages
- DNSSEC makes it more difficult for attackers to interfere with DNS operations, making the DNS system more robust overall.
- It can help in the prevention of phishing attempts by allowing users to validate the legitimacy of domain names and the websites to which they relate.
- DNSSEC ensures that DNS data is not altered during transmission, making it more reliable.
- It provides cryptographic security for DNS data, making cache poisoning and DNS spoofing attacks significantly more difficult.
Disadvantages
- DNSSEC implementation can be a difficult and time-consuming operation, especially for large or complex DNS zones.
- DNSSEC requires additional cryptographic processing, which can increase latency and affect DNS speed, i.e., affecting site performance and slowing it down.
- It’s not yet commonly used, although it’s already widely used by well-known companies, so it’s possible that some DNS services, devices, and software do not support it, leading to compatibility issues.
- More computing and storage resources are required to produce, sign, and validate DNSSEC records, which can be a problem for some companies.
Conclusion
In itself, using DNSSEC for your domain is important, especially if you have a large site that needs protection from cyber-attacks and phishing attempts, among other malicious practices that seek to steal user data or impersonate your domain to send spam or potentially dangerous files.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore the significance of DNSSEC in protecting internet users from DNS spoofing, cache poisoning, and other potential cyber threats.
Discover whether implementing DNSSEC is necessary for your website and how it can benefit your online presence.
Find out about the compatibility of DNSSEC with various domain names and registrars, and any potential limitations you should be aware of.
It enhances cybersecurity by adding a layer of authentication to DNS records. It prevents DNS spoofing and manipulation, ensuring the accuracy and integrity of domain lookups. This safeguards users from being redirected to malicious websites, enhancing online safety and trust.