In the dynamic landscape of digital communication, maintaining a healthy email deliverability is important for businesses and marketers seeking effective engagement with their audiences. The ability to reach recipient’s inboxes reliably not only ensures the successful delivery of messages but also plays a crucial role in building and sustaining positive relationships. Let’s understand Soft Bounces and hard Bounces in this article.
Also, Email deliverability is the measure of an email sender’s ability to deliver messages to the recipient’s inboxes without being flagged as spam or bouncing back. It goes beyond simply hitting the “send” button, it involves navigating through spam filters, avoiding blacklists, and fostering a positive sender reputation.
Achieving and sustaining a high level of email deliverability is fundamental for successful email marketing campaigns, ensuring that the right message reaches the right audience at the right time.
Understand the Basics of Email Warmp
Email Warmp, a strategic approach in email marketing, is designed to gradually establish and enhance a positive sender reputation when initiating or re-establishing email communication. This method involves systematically increasing email sending volumes over a specific period, allowing email service providers to recognize the sender as legitimate and trustworthy.
The primary purpose of Email Warmp is to mitigate the risk of emails being marked as spam, thereby maximizing deliverability and engagement with the intended audience.
Building and maintaining a positive sender reputation is the linchpin of successful email marketing. Email service providers evaluate sender reputations to determine whether emails should be delivered to the inbox, redirected to the spam folder, or rejected altogether.
A positive sender reputation is established through consistent adherence to best practices, including sending relevant and engaging content, minimizing bounce rates, and respecting recipient preferences.
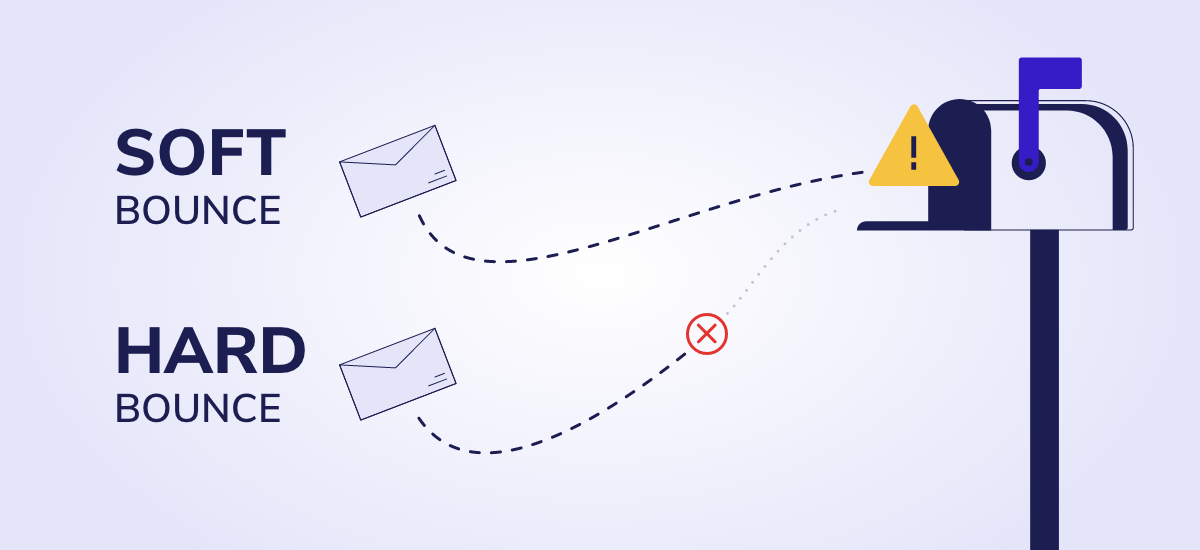
What is Soft Bounce?
Soft Bounces refer to temporary delivery failures that occur when an email cannot be delivered to the recipient’s inbox but is expected to be a transient issue.
Common Causes of Soft Bounces
Temporary Issues with the Recipient’s Mailbox:
Soft Bounces may occur when the recipient’s mailbox is temporarily full or has reached its storage limit. In such cases, the email server is unable to accept new messages until space is freed up, resulting in a temporary delivery failure.
Overloaded Email Server on the Recipient’s End:
Another common cause of Soft Bounces is an overloaded email server on the recipient’s end. When the server is experiencing high traffic or technical issues, it may temporarily be unable to accept incoming emails, leading to Soft Bounces.
Content-Related Issues Triggering Spam Filters:
Soft Bounces can also be triggered by content-related issues, such as emails being flagged by spam filters. If the email content contains elements that are commonly associated with spam, like certain keywords or formatting, it may result in a temporary failure to deliver the message.
Impact of Soft Bounces on Email Warmp
Soft Bounces, while generally temporary in nature, can impact the effectiveness of the Email Warmp strategy. Accumulating a high number of Soft Bounces may signal to email service providers that the sender’s list quality or email content needs attention.
This can potentially hinder the success of the Email Warmp process, as consistent delivery issues may negatively influence the sender’s reputation.
Strategies to Reduce Soft Bounces in the Email Warmp Process
Regularly Monitor Bounce Rates:
Keep a close eye on bounce rates during the Email Warmp process. Regular monitoring allows for the prompt identification of any increase in Soft Bounces, enabling quick corrective action.
Maintain a Clean Email List:
Regularly clean and update your email list to ensure it contains only valid and active email addresses. Remove addresses that consistently result in Soft Bounces, as continued attempts to deliver to these addresses can adversely affect sender’s reputation.
Optimize Email Content:
Review and optimize email content to minimize the risk of triggering spam filters. Avoid using spammy language, excessive punctuation, or other elements that may be flagged by email service providers.
Implement Retry Policies:
Configure your email system to implement retry policies for Soft Bounces. This means that the system will attempt to redeliver the email after a certain period, allowing for potential temporary issues to be resolved.
Provide Clear Instructions for Recipients:
Include clear instructions in your emails for recipients to address issues such as a full mailbox. Encourage them to free up space or take necessary actions to ensure successful future deliveries.
What is Hard Bounce?
Hard Bounces are definitive delivery failures that occur when an email cannot be delivered to the recipient’s inbox due to permanent issues.
Common Causes of Hard Bounces
Invalid or Non-Existent Email Addresses:
The most prevalent cause of Hard Bounces is attempting to send emails to email addresses that are either incorrectly formatted, misspelled or no longer exist. This can happen when an email address has been deactivated or abandoned by the user.
Domain-Related Issues:
Hard Bounces may occur when there are issues with the recipient’s domain. This can include misspelled or non-existent domains, or domains that have strict security measures in place, preventing successful email delivery.
Permanent Rejection by the Recipient’s Server:
Some email servers are configured to permanently reject emails from specific senders or domains. This could be a deliberate action by the recipient’s email service provider or server administrator to block unwanted or potentially harmful emails.
Impact of Hard Bounces on Email Warmp
Hard Bounces have a more significant impact on the Email Warmp strategy compared to Soft Bounces. Since Hard Bounces are indicative of persistent issues, accumulating a high number of them can adversely affect sender reputation and deliverability.
Email service providers interpret a high rate of Hard Bounces as a sign of poor list quality and may classify the sender as potentially engaging in spammy practices.
Minimize Hard Bounces and Maintain a Clean Email List
Regularly Clean and Update Email Lists:
Conduct regular audits of your email list to identify and remove invalid or non-existent email addresses. Keeping the list clean ensures that you are not attempting to send emails to addresses that are likely to result in Hard Bounces.
Implement Double Opt-In:
Use a double opt-in process when collecting email addresses. This requires users to confirm their subscription, reducing the likelihood of capturing invalid or mistyped email addresses.
Use Email Verification Tools:
Leverage email verification tools to validate the authenticity of email addresses before adding them to your list. These tools can help identify and filter out invalid or non-existent addresses.
Monitor and Address Bounce Rates Promptly:
Actively monitor bounce rates and promptly address any increase in Hard Bounces. Identify the root causes and take corrective actions to prevent further delivery failures.
Update DNS Records:
Ensure that your domain’s DNS records are correctly configured. Proper DNS settings are crucial for email delivery, and misconfigurations can lead to Hard Bounces.
How Email Warmp can Reduce Soft & Hard Bounces?
Email Warmp can effectively reduce both Soft and Hard Bounces by employing a strategic and gradual approach to building a positive sender reputation. Here’s how Email Warmp contributes to minimizing bounce rates:
- Gradual Volume Increase
- Recipient Engagement Monitoring
- Content Relevance and Quality
- Bounce Rate Management
- List Cleaning and Validation
Lastly, Email Warmp serves as a proactive strategy that allows senders to gradually establish a positive sender reputation, identify and address potential issues, and optimize their email practices to reduce both Soft and Hard Bounces. This careful and strategic approach contributes to improved email deliverability and the overall success of email marketing campaigns.